| Sustainability | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › journal papers › Sustainability |
Sustainability
|
Journals
Active Journals
Find a Journal
Proceedings Series
Topics
Information
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
Open Access Policy
Institutional Open Access Program
Special Issues Guidelines
Editorial Process
Research and Publication Ethics
Article Processing Charges
Awards
Testimonials
Author Services
Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
About
Overview
Contact
Careers
News
Blog
Sign In / Sign Up
Notice
clear
Notice
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader. Continue Cancel clearAll articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess. Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications. Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers. Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.  Journals
Active Journals
Find a Journal
Proceedings Series
Topics
Information
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
Open Access Policy
Institutional Open Access Program
Special Issues Guidelines
Editorial Process
Research and Publication Ethics
Article Processing Charges
Awards
Testimonials
Author Services
Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
About
Overview
Contact
Careers
News
Blog
Sign In / Sign Up
Submit
Journals
Active Journals
Find a Journal
Proceedings Series
Topics
Information
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
Open Access Policy
Institutional Open Access Program
Special Issues Guidelines
Editorial Process
Research and Publication Ethics
Article Processing Charges
Awards
Testimonials
Author Services
Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
About
Overview
Contact
Careers
News
Blog
Sign In / Sign Up
Submit
 5.0
5.0
 3.889
Journals
Sustainability
3.889
Journals
Sustainability
 Preliminary Approach for the Development of Sustainable University Campuses: A Case Study Based on the Mitigation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Preliminary Approach for the Development of Sustainable University Campuses: A Case Study Based on the Mitigation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
 The Influence of Sewage Sludge Composts on the Enzymatic Activity of Reclaimed Post-Mining Soil
The Influence of Sewage Sludge Composts on the Enzymatic Activity of Reclaimed Post-Mining Soil
 Environmental Assessment of Local Food Policies through a Territorial Life Cycle Approach
Environmental Assessment of Local Food Policies through a Territorial Life Cycle Approach
 Effect of Water Level Reduction on the Littoral Zone in Terms of Its Efficiency in Lake Protection
Journal Description
Sustainability
Sustainability
is an international, cross-disciplinary, scholarly, peer-reviewed and open access journal of environmental, cultural, economic, and social sustainability of human beings. It provides an advanced forum for studies related to sustainability and sustainable development, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Canadian Urban Transit Research & Innovation Consortium (CUTRIC) and International Council for Research and Innovation in Building and Construction (CIB) are affiliated with Sustainability and their members receive discounts of the article processing charge.
Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE and SSCI (Web of Science), GEOBASE, GeoRef, Inspec, AGRIS, RePEc, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Environmental Sciences) / CiteScore - Q1 (Geography, Planning and Development)
Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first
decision is provided to authors approximately 17.7 days after submission; acceptance
to publication is undertaken in 3.7 days (median values for papers published in
this journal in the second half of 2022).
Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Sustainability.
Companion journals for Sustainability include: World, Sustainable Chemistry, Conservation, Future Transportation, Architecture, Standards, Merits and Wind.
Impact Factor:
3.889 (2021);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.089 (2021)
subject
Imprint Information
get_app
Journal Flyer
Open Access
ISSN: 2071-1050
Latest Articles
get_app
subject
View online as:
Abstract Page
Full-Text HTML
Open AccessArticle
Carbon Neutrality Potential of Textile Products Made from Plant-Derived Fibers
by
Junran Liu, Shuyi Liu, Lisha Zhu, Lirong Sun, Ying Zhang, Xin Li and Laili Wang
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7070; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097070 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
During the growth of biomass, there are two carbon storage paths for plant-derived fibers. One path is to assimilate carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through photosynthesis and temporarily store it in textile plants. Besides, the carbon can be captured and
[...] Read more.
During the growth of biomass, there are two carbon storage paths for plant-derived fibers. One path is to assimilate carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through photosynthesis and temporarily store it in textile plants. Besides, the carbon can be captured and stored in soil. The carbon storage capacity of textile products made from plant-derived fibers such as cotton, flax, hemp, kenaf and bamboo fiber, etc., is a non-negligible part of greenhouse gas (GHG) accounting and reporting. However, there is a lack of systematic methods to evaluate carbon storage and the delayed emission effect of plant-derived fibers. In this study, the carbon storage and emission times of 100% hemp T-shirt, 100% hemp slipcover, and 100% hemp fiber handicraft were evaluated by using the soil organic carbon method, dry weight biomass method, and modeling method. The results revealed that the CO2 storage of 1 kg hemp fiber is 1.833 kg. Meanwhile, the delayed emission effects of carbon temporarily stored in the 3 kinds of hemp fiber products are 3.83%, 19.68%, and 41.12% at different lifespans (i.e., 5, 25, or 50 years), in which case the landfill option for hemp fiber products may be preferable from carbon storage effect perspective. The results suggest that plant-derived fibers have a positive impact on climate change due to CO2 storage, and that the carbon storage effect improves with the continued lifespan of the product. By quantifying carbon storage and the delayed emission effect of plant-derived fibers, it is beneficial to understand the potential for reducing carbon emissions, which in turn helps to promote and develop more environmentally friendly and low-carbon production processes and products.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainability in Textiles)
►▼
Show Figures
Effect of Water Level Reduction on the Littoral Zone in Terms of Its Efficiency in Lake Protection
Journal Description
Sustainability
Sustainability
is an international, cross-disciplinary, scholarly, peer-reviewed and open access journal of environmental, cultural, economic, and social sustainability of human beings. It provides an advanced forum for studies related to sustainability and sustainable development, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Canadian Urban Transit Research & Innovation Consortium (CUTRIC) and International Council for Research and Innovation in Building and Construction (CIB) are affiliated with Sustainability and their members receive discounts of the article processing charge.
Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE and SSCI (Web of Science), GEOBASE, GeoRef, Inspec, AGRIS, RePEc, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Environmental Sciences) / CiteScore - Q1 (Geography, Planning and Development)
Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first
decision is provided to authors approximately 17.7 days after submission; acceptance
to publication is undertaken in 3.7 days (median values for papers published in
this journal in the second half of 2022).
Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Sustainability.
Companion journals for Sustainability include: World, Sustainable Chemistry, Conservation, Future Transportation, Architecture, Standards, Merits and Wind.
Impact Factor:
3.889 (2021);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.089 (2021)
subject
Imprint Information
get_app
Journal Flyer
Open Access
ISSN: 2071-1050
Latest Articles
get_app
subject
View online as:
Abstract Page
Full-Text HTML
Open AccessArticle
Carbon Neutrality Potential of Textile Products Made from Plant-Derived Fibers
by
Junran Liu, Shuyi Liu, Lisha Zhu, Lirong Sun, Ying Zhang, Xin Li and Laili Wang
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7070; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097070 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
During the growth of biomass, there are two carbon storage paths for plant-derived fibers. One path is to assimilate carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through photosynthesis and temporarily store it in textile plants. Besides, the carbon can be captured and
[...] Read more.
During the growth of biomass, there are two carbon storage paths for plant-derived fibers. One path is to assimilate carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through photosynthesis and temporarily store it in textile plants. Besides, the carbon can be captured and stored in soil. The carbon storage capacity of textile products made from plant-derived fibers such as cotton, flax, hemp, kenaf and bamboo fiber, etc., is a non-negligible part of greenhouse gas (GHG) accounting and reporting. However, there is a lack of systematic methods to evaluate carbon storage and the delayed emission effect of plant-derived fibers. In this study, the carbon storage and emission times of 100% hemp T-shirt, 100% hemp slipcover, and 100% hemp fiber handicraft were evaluated by using the soil organic carbon method, dry weight biomass method, and modeling method. The results revealed that the CO2 storage of 1 kg hemp fiber is 1.833 kg. Meanwhile, the delayed emission effects of carbon temporarily stored in the 3 kinds of hemp fiber products are 3.83%, 19.68%, and 41.12% at different lifespans (i.e., 5, 25, or 50 years), in which case the landfill option for hemp fiber products may be preferable from carbon storage effect perspective. The results suggest that plant-derived fibers have a positive impact on climate change due to CO2 storage, and that the carbon storage effect improves with the continued lifespan of the product. By quantifying carbon storage and the delayed emission effect of plant-derived fibers, it is beneficial to understand the potential for reducing carbon emissions, which in turn helps to promote and develop more environmentally friendly and low-carbon production processes and products.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainability in Textiles)
►▼
Show Figures
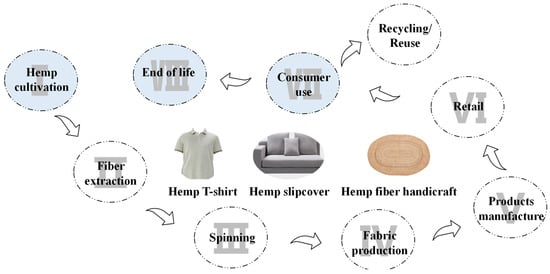 Figure 1 get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessArticle Access and Control of Resources and Participation in Rice-Breeding Activities among Men and Women Farmers in Southern Ghana by Bright Owusu Asante, Ranjitha Puskur, Elizabeth Garner, Margaret Najjingo Mangheni, Richard Adabah, Maxwell Darko Asante, Benedicta Nsiah Frimpong and Stephen Prah Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7069; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097069 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023 Abstract This paper provides evidence of gender differences in the access and control of resources and their relation to participation in rice-breeding activities among men and women farmers in southern Ghana. We used a mixed methods design which involved the use of qualitative data [...] Read more. This paper provides evidence of gender differences in the access and control of resources and their relation to participation in rice-breeding activities among men and women farmers in southern Ghana. We used a mixed methods design which involved the use of qualitative data collected through focus group discussions (FGDs) and key informant interviews (KIIs) and quantitative data collection through a survey. Using data collected from 315 smallholder rice farmers, perception analyses and probit and multivariate regression were employed in the analyses. Our findings indicate that higher levels of education, experience in rice farming, a favorable dependency ratio, larger farm size, more rice plots, access to extension services, and involvement with financial organizations positively influence participation in rice-breeding activities. On the other hand, distance to market is found to have a negative impact on participation. Moreover, years of education, experience in rice farming, farm size, number of rice plots, dependency ratio, and distance to market were found to negatively influence the control of production resources among both male and female participants in rice-breeding activities. From both the quantitative and qualitative results, men had more access to productive resources than women. Insights from this study will enhance gender equity in promoting the participation of both men and women in rice varietal development activities. Full article (This article belongs to the Special Issue Gender-Responsive Crop Improvement: From Great Training to Evidence from the Field) ►▼ Show Figures Figure 1 get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessArticle Evaluating and Prioritizing the Green Infrastructure Finance Risks for Sustainable Development in China by Yan Dai and Yan Dai and  Yasir Ahmed Solangi
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7068; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097068 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
China has become a global leader in green infrastructure finance, investing heavily in renewable energy, sustainable transportation, and green buildings. However, there are multiple risks and challenges that impede the development of green infrastructure finance. Thus, this study analyzes and prioritizes the risks
[...] Read more.
China has become a global leader in green infrastructure finance, investing heavily in renewable energy, sustainable transportation, and green buildings. However, there are multiple risks and challenges that impede the development of green infrastructure finance. Thus, this study analyzes and prioritizes the risks associated with green infrastructure finance in China and proposes policy plans to mitigate these risks. A Fuzzy analytical hierarchy process (AHP) is used to identify the main risks associated with green infrastructure finance. The main risks are further decomposed into sub-risks. After, the Fuzzy VlseKriterijumska Optimizacija I Kompromisno Resenje (VIKOR) method is used to prioritize the key policy plans to mitigate risks and sub-risks. The results of Fuzzy AHP show that policy and regulations are the most significant risk associated with green infrastructure finance in China, followed by financial risks, and technical risks. The results of Fuzzy VIKOR reveal that increasing the availability of financing options is the most crucial policy plan to mitigate the risks and sub-risks for green infrastructure finance. The developed standardized technical guidelines and procedures and a legal and regulatory framework are ranked second and third are the most effective and feasible policy plans.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Finance and Risk Management)
►▼
Show Figures Yasir Ahmed Solangi
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7068; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097068 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
China has become a global leader in green infrastructure finance, investing heavily in renewable energy, sustainable transportation, and green buildings. However, there are multiple risks and challenges that impede the development of green infrastructure finance. Thus, this study analyzes and prioritizes the risks
[...] Read more.
China has become a global leader in green infrastructure finance, investing heavily in renewable energy, sustainable transportation, and green buildings. However, there are multiple risks and challenges that impede the development of green infrastructure finance. Thus, this study analyzes and prioritizes the risks associated with green infrastructure finance in China and proposes policy plans to mitigate these risks. A Fuzzy analytical hierarchy process (AHP) is used to identify the main risks associated with green infrastructure finance. The main risks are further decomposed into sub-risks. After, the Fuzzy VlseKriterijumska Optimizacija I Kompromisno Resenje (VIKOR) method is used to prioritize the key policy plans to mitigate risks and sub-risks. The results of Fuzzy AHP show that policy and regulations are the most significant risk associated with green infrastructure finance in China, followed by financial risks, and technical risks. The results of Fuzzy VIKOR reveal that increasing the availability of financing options is the most crucial policy plan to mitigate the risks and sub-risks for green infrastructure finance. The developed standardized technical guidelines and procedures and a legal and regulatory framework are ranked second and third are the most effective and feasible policy plans.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Finance and Risk Management)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessArticle Sustainable Logistics 4.0: A Study on Selecting the Best Technology for Internal Material Handling by Saverio Ferraro, Saverio Ferraro,  Alessandra Cantini, Alessandra Cantini,  Leonardo Leoni and Leonardo Leoni and  Filippo De Carlo
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7067; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097067 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
Logistics is a vital activity for the economic growth of an organization as it manages the flow of materials and information within, into, and out of the organization, as well as reverse flow. Like many other industrial processes, logistics has also been impacted
[...] Read more.
Logistics is a vital activity for the economic growth of an organization as it manages the flow of materials and information within, into, and out of the organization, as well as reverse flow. Like many other industrial processes, logistics has also been impacted by the rise of Industry 4.0 technologies, which has highlighted the significance of Logistics 4.0. However, Logistics 4.0 is mainly focused on economic benefits, while overlooking environmental and social concerns. To address this, a method is proposed that takes into account the three goals of sustainable development when selecting the best technology for internal material handling activities. Firstly, a comprehensive literature review was conducted to examine the application of 4.0 technologies in logistics processes and their impact on economic, environmental, and social sustainability. Secondly, based on the findings of the review, a three-level analytic hierarchy process was proposed to identify the optimal 4.0 technology for internal logistics. To demonstrate the practicality of the proposed method, it was tested on three companies. The results showed that additive manufacturing, exoskeletons, and collaborative robots are the most suitable options for achieving sustainable development goals within Logistics 4.0.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Complicated Relationship between Innovation and Sustainability: Opportunities, Threats, Challenges, and Trends)
►▼
Show Figures Filippo De Carlo
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7067; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097067 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
Logistics is a vital activity for the economic growth of an organization as it manages the flow of materials and information within, into, and out of the organization, as well as reverse flow. Like many other industrial processes, logistics has also been impacted
[...] Read more.
Logistics is a vital activity for the economic growth of an organization as it manages the flow of materials and information within, into, and out of the organization, as well as reverse flow. Like many other industrial processes, logistics has also been impacted by the rise of Industry 4.0 technologies, which has highlighted the significance of Logistics 4.0. However, Logistics 4.0 is mainly focused on economic benefits, while overlooking environmental and social concerns. To address this, a method is proposed that takes into account the three goals of sustainable development when selecting the best technology for internal material handling activities. Firstly, a comprehensive literature review was conducted to examine the application of 4.0 technologies in logistics processes and their impact on economic, environmental, and social sustainability. Secondly, based on the findings of the review, a three-level analytic hierarchy process was proposed to identify the optimal 4.0 technology for internal logistics. To demonstrate the practicality of the proposed method, it was tested on three companies. The results showed that additive manufacturing, exoskeletons, and collaborative robots are the most suitable options for achieving sustainable development goals within Logistics 4.0.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Complicated Relationship between Innovation and Sustainability: Opportunities, Threats, Challenges, and Trends)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 attachment Supplementary material: Supplementary File 1 (ZIP, 1727 KiB) get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessArticle Enset Production System Diversity across the Southern Ethiopian Highlands by Guy Blomme, Guy Blomme,  Elizabeth Kearsley, Elizabeth Kearsley,  Sisay Buta, Sisay Buta,  Alemayehu Chala, Alemayehu Chala,  Ruhama Kebede, Ruhama Kebede,  Temesgen Addis and Temesgen Addis and  Zerihun Yemataw
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7066; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097066 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
Enset is a staple crop of the southern Ethiopian highlands. Small-holder farmers cultivate enset as part of mixed subsistence farming systems, in which enset provides substantial food security services. While its cultivation is unique to this region, enset production systems take on many
[...] Read more.
Enset is a staple crop of the southern Ethiopian highlands. Small-holder farmers cultivate enset as part of mixed subsistence farming systems, in which enset provides substantial food security services. While its cultivation is unique to this region, enset production systems take on many forms, varying with environmental and agronomic conditions, crop diversity and (co-)staples produced, the importance of enset for the household, and socio-economic and cultural differences. Through extensive interviews with 375 households covering 20 communities, along an altitudinal range of 1500 to 3000 masl across the main enset-producing belt, the diversity in enset production systems was assessed. We show that the size of enset-producing land holdings and the overall cultivated farmland decreased with altitude. The economic status of households however drives the proportion of land allocated to enset, with relatively more land (45%) allocated to the cultivation of enset in poorer households compared to medium (38%) and to richer (23%) households. The food crop diversity, with an average of 6.4 different food crop species on a farm (ranging from 2 to 15 crops), did not vary with the wealth status of the households or with altitude. Enset-derived food items were a main component of multiple daily meals for most households, complemented with other crops produced on the farm. Supplemental food purchases mainly included meat and bread products, although the purchasing power of enset-growing households is predominantly low. The co-staples grown varied with altitude, according to crop productive cultivation boundaries. Maize was an important co-staple observed across the entire investigated altitudinal range. At the mid to upper altitudes, wheat and barley often supplemented or substituted maize as the main cereal crop, while at the mid to lower altitudes, teff was produced in addition to maize. Coffee was the main cash crop grown up to altitudes of 2300 m. Root and tuber crops, and legumes had a more moderate importance in these systems. At lower altitudes, yam, sweet potato and taro were the main roots and tubers produced, which shifted to Irish potatoes at the mid to high altitudes. The importance of beans was higher in several high-altitude kebeles. The food crop diversity, combined with livestock rearing are key for the self-reliance of the small-holder subsistence farms. The need for increased enset cultivation was highlighted by the farmers to ensure food availability and food security with population growth. On the other hand, enset cultivation was mainly threatened by Xanthomonas wilt.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures Zerihun Yemataw
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7066; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097066 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
Enset is a staple crop of the southern Ethiopian highlands. Small-holder farmers cultivate enset as part of mixed subsistence farming systems, in which enset provides substantial food security services. While its cultivation is unique to this region, enset production systems take on many
[...] Read more.
Enset is a staple crop of the southern Ethiopian highlands. Small-holder farmers cultivate enset as part of mixed subsistence farming systems, in which enset provides substantial food security services. While its cultivation is unique to this region, enset production systems take on many forms, varying with environmental and agronomic conditions, crop diversity and (co-)staples produced, the importance of enset for the household, and socio-economic and cultural differences. Through extensive interviews with 375 households covering 20 communities, along an altitudinal range of 1500 to 3000 masl across the main enset-producing belt, the diversity in enset production systems was assessed. We show that the size of enset-producing land holdings and the overall cultivated farmland decreased with altitude. The economic status of households however drives the proportion of land allocated to enset, with relatively more land (45%) allocated to the cultivation of enset in poorer households compared to medium (38%) and to richer (23%) households. The food crop diversity, with an average of 6.4 different food crop species on a farm (ranging from 2 to 15 crops), did not vary with the wealth status of the households or with altitude. Enset-derived food items were a main component of multiple daily meals for most households, complemented with other crops produced on the farm. Supplemental food purchases mainly included meat and bread products, although the purchasing power of enset-growing households is predominantly low. The co-staples grown varied with altitude, according to crop productive cultivation boundaries. Maize was an important co-staple observed across the entire investigated altitudinal range. At the mid to upper altitudes, wheat and barley often supplemented or substituted maize as the main cereal crop, while at the mid to lower altitudes, teff was produced in addition to maize. Coffee was the main cash crop grown up to altitudes of 2300 m. Root and tuber crops, and legumes had a more moderate importance in these systems. At lower altitudes, yam, sweet potato and taro were the main roots and tubers produced, which shifted to Irish potatoes at the mid to high altitudes. The importance of beans was higher in several high-altitude kebeles. The food crop diversity, combined with livestock rearing are key for the self-reliance of the small-holder subsistence farms. The need for increased enset cultivation was highlighted by the farmers to ensure food availability and food security with population growth. On the other hand, enset cultivation was mainly threatened by Xanthomonas wilt.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Open AccessArticle Biodiversity and Resilience to Tsunamis in Chilean Urban Areas: The Role of Ecoinformatics by Mariana Brüning-González, Mariana Brüning-González,  Paula Villagra and Paula Villagra and  Horacio Samaniego
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7065; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097065 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
By definition, a smart city must improve its readiness for extreme events in order to confront the growing unpredictability of natural disasters. Doing this implies planning for resilience. That is, to enhance our capacity to cope, mitigate, adapt, and rebuild human settlements after
[...] Read more.
By definition, a smart city must improve its readiness for extreme events in order to confront the growing unpredictability of natural disasters. Doing this implies planning for resilience. That is, to enhance our capacity to cope, mitigate, adapt, and rebuild human settlements after a catastrophic event. Although scholars have argued that biodiversity can enhance resilience, there is a dearth of empirical research that specifically addresses this crucial issue. This research analyzes Nature’s Contributions to People related to tsunami resilience. Then, the relationship between biodiversity and community resilience indexes is examined for 50 coastal Chilean cities that are prone to tsunamis, using biodiversity data from an open access database. The resilience index "population living in the first kilometer from the shoreline" was found to be correlated with species richness (ρ = 0.48) and the evenness biodiversity index, Pielou (ρ = −0.47). These results suggest that biodiversity data availability is crucial for understanding nature’s contribution to human settlement resilience. Although this study was hindered by limited data availability, the potential use in other contexts remains valuable for the development of smart cities. The study highlights the need for increased biodiversity data collection on a national scale and emphasizes the use of ecoinformatics to create smart cities that can effectively respond to climate uncertainty in coastal urban areas.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Cities, Biodiversity and Green Infrastructure - Living Dimensions of Future Cities)
get_app
subject
View online as:
Abstract Page
Full-Text HTML
Open AccessArticle
Life Cycle Assessment of High-Performance Railway Infrastructure, Analysis of Superstructures in Tunnels and on Open Tracks
by Horacio Samaniego
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7065; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097065 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
By definition, a smart city must improve its readiness for extreme events in order to confront the growing unpredictability of natural disasters. Doing this implies planning for resilience. That is, to enhance our capacity to cope, mitigate, adapt, and rebuild human settlements after
[...] Read more.
By definition, a smart city must improve its readiness for extreme events in order to confront the growing unpredictability of natural disasters. Doing this implies planning for resilience. That is, to enhance our capacity to cope, mitigate, adapt, and rebuild human settlements after a catastrophic event. Although scholars have argued that biodiversity can enhance resilience, there is a dearth of empirical research that specifically addresses this crucial issue. This research analyzes Nature’s Contributions to People related to tsunami resilience. Then, the relationship between biodiversity and community resilience indexes is examined for 50 coastal Chilean cities that are prone to tsunamis, using biodiversity data from an open access database. The resilience index "population living in the first kilometer from the shoreline" was found to be correlated with species richness (ρ = 0.48) and the evenness biodiversity index, Pielou (ρ = −0.47). These results suggest that biodiversity data availability is crucial for understanding nature’s contribution to human settlement resilience. Although this study was hindered by limited data availability, the potential use in other contexts remains valuable for the development of smart cities. The study highlights the need for increased biodiversity data collection on a national scale and emphasizes the use of ecoinformatics to create smart cities that can effectively respond to climate uncertainty in coastal urban areas.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Cities, Biodiversity and Green Infrastructure - Living Dimensions of Future Cities)
get_app
subject
View online as:
Abstract Page
Full-Text HTML
Open AccessArticle
Life Cycle Assessment of High-Performance Railway Infrastructure, Analysis of Superstructures in Tunnels and on Open Tracks
by
 Lukas Hausberger, Lukas Hausberger,  Tobias Cordes and Tobias Cordes and  Florian Gschösser
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7064; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097064 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
Almost 25% of the environmental pollution, measured by the indicator of global greenhouse emissions, is emitted by transport. Changes in the mobility behavior of the population will be essential if the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the goals of the EU
[...] Read more.
Almost 25% of the environmental pollution, measured by the indicator of global greenhouse emissions, is emitted by transport. Changes in the mobility behavior of the population will be essential if the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the goals of the EU Commission’s Green Deal are to be attained. Accordingly, the existing infrastructure has to transform into a sustainable transport infrastructure through further optimizations in the future. Therefore, continuous optimizations and improvements of designs, materials, and processes are crucial to achieving long-term sustainability. This study investigates different superstructures with the method of life cycle assessment using the example of the emerging high-performance infrastructure at the Brenner Base Tunnel (BBT). The study analyzes all relevant life cycle stages (A1–C4) and validates different effects of service lifetimes of superstructure elements on the open track and in the tunnel. The results, which are presented in the form of GWP, AP, and NRCED, show that there is environmental reduction potential, especially in the stage of use. As more frequent modernization cycles and the associated remanufacturing of superstructure elements account for a significant proportion of the total environmental impact, lifetime extending optimization of products yields improvements in the ecological footprint.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Development of Construction Management and Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures Florian Gschösser
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7064; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097064 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
Almost 25% of the environmental pollution, measured by the indicator of global greenhouse emissions, is emitted by transport. Changes in the mobility behavior of the population will be essential if the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the goals of the EU
[...] Read more.
Almost 25% of the environmental pollution, measured by the indicator of global greenhouse emissions, is emitted by transport. Changes in the mobility behavior of the population will be essential if the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the goals of the EU Commission’s Green Deal are to be attained. Accordingly, the existing infrastructure has to transform into a sustainable transport infrastructure through further optimizations in the future. Therefore, continuous optimizations and improvements of designs, materials, and processes are crucial to achieving long-term sustainability. This study investigates different superstructures with the method of life cycle assessment using the example of the emerging high-performance infrastructure at the Brenner Base Tunnel (BBT). The study analyzes all relevant life cycle stages (A1–C4) and validates different effects of service lifetimes of superstructure elements on the open track and in the tunnel. The results, which are presented in the form of GWP, AP, and NRCED, show that there is environmental reduction potential, especially in the stage of use. As more frequent modernization cycles and the associated remanufacturing of superstructure elements account for a significant proportion of the total environmental impact, lifetime extending optimization of products yields improvements in the ecological footprint.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Development of Construction Management and Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 attachment Supplementary material: Supplementary File 1 (ZIP, 12134 KiB) get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessReview Desalination of Saline Irrigation Water Using Hydrophobic, Metal–Polymer Hydrogels by David D. J. Antia
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7063; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097063 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
Saline irrigation water accounts for 15% to 30% of global, anthropogenic, water usage, and around 10% to 15% of global arable food production. Decreasing the salinity of this irrigation water has the potential to substantially increase the yields associated with these crops. In
[...] Read more.
Saline irrigation water accounts for 15% to 30% of global, anthropogenic, water usage, and around 10% to 15% of global arable food production. Decreasing the salinity of this irrigation water has the potential to substantially increase the yields associated with these crops. In this paper, 87 sol–gel hydrophobic and supra-hydrophobic, hollow, metal, hydroxyoxide and polymer formulations (constructed using inexpensive, agricultural chemicals) were demonstrated to remove Na+ ions and Cl− ions from saline water. The process operates without producing a waste brine or requiring an external energy source and is designed to desalinate water within existing tanks and impoundments. The desalination results of the polymer were combined with the salinity reduction profiles of 70 crops suitable for cultivation, including arable, orchard, horticultural, and livestock forage crops. The analysis established that use of the desalinated water may result in both substantial increases in crop yield, and an increase in the variety of crops that can be grown. Analysis of the ion removal process established a novel methodology for assessing the salinity of the product water. This methodology allows the salinity of the product water to be determined from a combination of EC (electrical conductivity) and pH measurements.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Technologies, Techniques and Process for the Sustainable Precision Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures David D. J. Antia
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7063; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097063 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
Saline irrigation water accounts for 15% to 30% of global, anthropogenic, water usage, and around 10% to 15% of global arable food production. Decreasing the salinity of this irrigation water has the potential to substantially increase the yields associated with these crops. In
[...] Read more.
Saline irrigation water accounts for 15% to 30% of global, anthropogenic, water usage, and around 10% to 15% of global arable food production. Decreasing the salinity of this irrigation water has the potential to substantially increase the yields associated with these crops. In this paper, 87 sol–gel hydrophobic and supra-hydrophobic, hollow, metal, hydroxyoxide and polymer formulations (constructed using inexpensive, agricultural chemicals) were demonstrated to remove Na+ ions and Cl− ions from saline water. The process operates without producing a waste brine or requiring an external energy source and is designed to desalinate water within existing tanks and impoundments. The desalination results of the polymer were combined with the salinity reduction profiles of 70 crops suitable for cultivation, including arable, orchard, horticultural, and livestock forage crops. The analysis established that use of the desalinated water may result in both substantial increases in crop yield, and an increase in the variety of crops that can be grown. Analysis of the ion removal process established a novel methodology for assessing the salinity of the product water. This methodology allows the salinity of the product water to be determined from a combination of EC (electrical conductivity) and pH measurements.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Technologies, Techniques and Process for the Sustainable Precision Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessArticle The Sustainable Rural Industrial Development under Entrepreneurship and Deep Learning from Digital Empowerment by Suwei Gao, Suwei Gao,  Xiaobei Yang, Xiaobei Yang,  Huizhen Long, Huizhen Long,  Fengrui Zhang and Fengrui Zhang and  Qin Xin
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7062; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097062 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
This paper aims to realize the planning of resource utilization and development of rural industries endowed by digitalization under entrepreneurship. First, the global classic practical experience of digitizing rural industries is studied, and the development model of existing rural industries is captured from
[...] Read more.
This paper aims to realize the planning of resource utilization and development of rural industries endowed by digitalization under entrepreneurship. First, the global classic practical experience of digitizing rural industries is studied, and the development model of existing rural industries is captured from the perspective of entrepreneurship. Second, the influencing factors of rural industrial development are extracted, the structure of resource development is analyzed, and a Neural Network (NN) model of industrial development aiming at expected per capita annual income is established. In addition, a Genetic Algorithm (GA) is introduced to learn the weights of influencing factors in the model. The structure of the NN is determined through extensive experiments. Finally, conclusions are drawn through the simulation and experiment of NN and GA. Tourism, infrastructure, and transportation planning have weights of 7.79, 5.6, and 6.4, respectively, and these three sectors should be vigorously developed. In the future, the weight values of these factors can be used for reference, and the development of various aspects can be refined. This paper clarifies the core of industrial development in rural revitalization based on the perspective of entrepreneurship. The problem of how to realize the optimal utilization of resources is solved scientifically and rationally through the mathematical model. The introduction of deep learning algorithm models provides data support for resource allocation and industrial planning in the process of digital empowerment of traditional rural industries, which is of great value and significance for exploring digital models for rural industry development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Digital Transformation of Agriculture and Rural Areas)
►▼
Show Figures Qin Xin
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7062; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097062 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
This paper aims to realize the planning of resource utilization and development of rural industries endowed by digitalization under entrepreneurship. First, the global classic practical experience of digitizing rural industries is studied, and the development model of existing rural industries is captured from
[...] Read more.
This paper aims to realize the planning of resource utilization and development of rural industries endowed by digitalization under entrepreneurship. First, the global classic practical experience of digitizing rural industries is studied, and the development model of existing rural industries is captured from the perspective of entrepreneurship. Second, the influencing factors of rural industrial development are extracted, the structure of resource development is analyzed, and a Neural Network (NN) model of industrial development aiming at expected per capita annual income is established. In addition, a Genetic Algorithm (GA) is introduced to learn the weights of influencing factors in the model. The structure of the NN is determined through extensive experiments. Finally, conclusions are drawn through the simulation and experiment of NN and GA. Tourism, infrastructure, and transportation planning have weights of 7.79, 5.6, and 6.4, respectively, and these three sectors should be vigorously developed. In the future, the weight values of these factors can be used for reference, and the development of various aspects can be refined. This paper clarifies the core of industrial development in rural revitalization based on the perspective of entrepreneurship. The problem of how to realize the optimal utilization of resources is solved scientifically and rationally through the mathematical model. The introduction of deep learning algorithm models provides data support for resource allocation and industrial planning in the process of digital empowerment of traditional rural industries, which is of great value and significance for exploring digital models for rural industry development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Digital Transformation of Agriculture and Rural Areas)
►▼
Show Figures
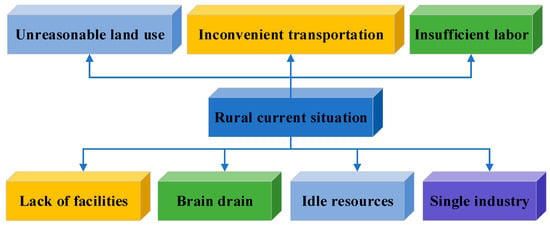 Figure 1 attachment Supplementary material: Supplementary File 1 (ZIP, 390 KiB) get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessSystematic Review Knowledge, Competencies, and Skills for a Sustainable Sport Management Growth: A Systematic Review by Flavia Guidotti, Flavia Guidotti,  Sabrina Demarie, Sabrina Demarie,  Simone Ciaccioni and Simone Ciaccioni and  Laura Capranica
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7061; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097061 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
The present systematic review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of sport management relevant knowledge, competencies, and skills analyzing and harmonizing the European skills classification for sport management employment profiles and evidence-based information from the scientific literature in this field. The information search
[...] Read more.
The present systematic review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of sport management relevant knowledge, competencies, and skills analyzing and harmonizing the European skills classification for sport management employment profiles and evidence-based information from the scientific literature in this field. The information search in the European Skills, Competences, Qualifications and Occupations platform resulted in four main sport management professional profiles, whereas literature searches in SPORTDiscus (EBSCOhost), Scopus, and Google Scholar databases resulted in 48 manuscripts meeting the inclusion criteria. The main findings showed a substantial scholars’ interest in deepening the understanding of necessary sport management-related knowledge/competencies/skills from different research perspectives. However, a disconnect between industry demands and students and/or employees’ preparedness and performance emerged, which substantiates the need to systematically update education and training in the sector to foster the sustainable development of this scientific area. Furthermore, in recognizing the centrality of the background, foundational, sport management-related knowledge, the crucial role of competencies and soft skills emerged. The present study not only provided a comprehensive, evidence-based, overview on sport management relevant knowledge/competencies/skills but also proposed a harmonized framework grounded on different relevant clusters that should be considered in developing and implementing educational sustainable programs for sport managers and leaders.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures Laura Capranica
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7061; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097061 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
The present systematic review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of sport management relevant knowledge, competencies, and skills analyzing and harmonizing the European skills classification for sport management employment profiles and evidence-based information from the scientific literature in this field. The information search
[...] Read more.
The present systematic review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of sport management relevant knowledge, competencies, and skills analyzing and harmonizing the European skills classification for sport management employment profiles and evidence-based information from the scientific literature in this field. The information search in the European Skills, Competences, Qualifications and Occupations platform resulted in four main sport management professional profiles, whereas literature searches in SPORTDiscus (EBSCOhost), Scopus, and Google Scholar databases resulted in 48 manuscripts meeting the inclusion criteria. The main findings showed a substantial scholars’ interest in deepening the understanding of necessary sport management-related knowledge/competencies/skills from different research perspectives. However, a disconnect between industry demands and students and/or employees’ preparedness and performance emerged, which substantiates the need to systematically update education and training in the sector to foster the sustainable development of this scientific area. Furthermore, in recognizing the centrality of the background, foundational, sport management-related knowledge, the crucial role of competencies and soft skills emerged. The present study not only provided a comprehensive, evidence-based, overview on sport management relevant knowledge/competencies/skills but also proposed a harmonized framework grounded on different relevant clusters that should be considered in developing and implementing educational sustainable programs for sport managers and leaders.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessArticle From Hazardous Chrysotile and Polyamide Wastes into Sustainable Serpentine/Polyamide Nanocomposite Membrane: Fabrication, Characterization, and Environmental Application by Amal H. El Maghrabi, Amal H. El Maghrabi,  Mohmmed M. El-Rabiee, Mohmmed M. El-Rabiee,  Bahaa S. Metwally, Bahaa S. Metwally,  Mostafa A. Masoud, Mostafa A. Masoud,  Mohamed H. Abdelaziz, Mohamed H. Abdelaziz,  Petros Petrounias, Petros Petrounias,  Nikolaos Koukouzas and Nikolaos Koukouzas and  Ahmed M. Zayed
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7060; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097060 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
Sustainable serpentine/polyamide nanocomposite (SP/PAM) was fabricated using malicious mining (serpentine chrysotile, SP Ctl) and industrial (polyamide, PA6) wastes via the electro-spinning technique. Before fabrication, the fibrous nature of Ctl was demolished through intensive grinding into nano-fractions. The successful impregnation of Ctl within PA6
[...] Read more.
Sustainable serpentine/polyamide nanocomposite (SP/PAM) was fabricated using malicious mining (serpentine chrysotile, SP Ctl) and industrial (polyamide, PA6) wastes via the electro-spinning technique. Before fabrication, the fibrous nature of Ctl was demolished through intensive grinding into nano-fractions. The successful impregnation of Ctl within PA6 via the electro-spinning technique at fixed ratios of precursor raw materials in the dissolving agent (7.5/92.5% SP/PA wt/wt solid/solid) created an internal network structure within the polymer fibers by molecular self-assembly. SP/PAM showcased its prowess in tackling the remediation of diverse dyes and Fe(III) from synthetic solutions in a batch system. Based on correlation coefficient outcomes (R2 ≈ 0.999), the pseudo-second-order equation justified the sorption data in an adequate way for all contaminants. In addition, intra-particle diffusion was not the only driving factor in the sorption process. Similarly, the Langmuir equation with maximum removal capacity (qmax) 5.97, 4.33, and 5.36 mg/g for MO, MB, and Fe(Ⅲ), respectively, defined the sorption data better than Freundlich.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Technologies and Materials for Wastewater Treatment and Reclamation)
►▼
Show Figures Ahmed M. Zayed
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7060; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097060 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
Sustainable serpentine/polyamide nanocomposite (SP/PAM) was fabricated using malicious mining (serpentine chrysotile, SP Ctl) and industrial (polyamide, PA6) wastes via the electro-spinning technique. Before fabrication, the fibrous nature of Ctl was demolished through intensive grinding into nano-fractions. The successful impregnation of Ctl within PA6
[...] Read more.
Sustainable serpentine/polyamide nanocomposite (SP/PAM) was fabricated using malicious mining (serpentine chrysotile, SP Ctl) and industrial (polyamide, PA6) wastes via the electro-spinning technique. Before fabrication, the fibrous nature of Ctl was demolished through intensive grinding into nano-fractions. The successful impregnation of Ctl within PA6 via the electro-spinning technique at fixed ratios of precursor raw materials in the dissolving agent (7.5/92.5% SP/PA wt/wt solid/solid) created an internal network structure within the polymer fibers by molecular self-assembly. SP/PAM showcased its prowess in tackling the remediation of diverse dyes and Fe(III) from synthetic solutions in a batch system. Based on correlation coefficient outcomes (R2 ≈ 0.999), the pseudo-second-order equation justified the sorption data in an adequate way for all contaminants. In addition, intra-particle diffusion was not the only driving factor in the sorption process. Similarly, the Langmuir equation with maximum removal capacity (qmax) 5.97, 4.33, and 5.36 mg/g for MO, MB, and Fe(Ⅲ), respectively, defined the sorption data better than Freundlich.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Technologies and Materials for Wastewater Treatment and Reclamation)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessArticle Measuring River-View Visibilities of Individual Dwellings for Planning of Compact Urban Riverside Neighborhood Blocks by Yang Guo, Yang Guo,  Dongchi Lai and Dongchi Lai and  Xijun Hu
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7059; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097059 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
Line-of-sight occlusion in compact cities commonly reduces the river views of riverfront residents. This study developed a new approach to measure the river-view visibilities of individual dwellings in urban riverfront neighborhood blocks. The objective of this study is to achieve a good integration
[...] Read more.
Line-of-sight occlusion in compact cities commonly reduces the river views of riverfront residents. This study developed a new approach to measure the river-view visibilities of individual dwellings in urban riverfront neighborhood blocks. The objective of this study is to achieve a good integration between the morphology of building groups and the ideal river-view visibility of dwellings, and to provide assistance in building and landscape design through the proposed method. First, a design case of an actual riverside neighborhood block with two initial building layout schemes was selected. The complex layout scheme led to a better building-group morphology than the simple layout scheme. Second, 3D models were built using the Rhinoceros and Grasshopper software platforms, and 3D isovists were generated on the hypothetical River Surface Curve (RSC) equipartition points. Finally, the data from the 3D isovists were used to measure the river-view visibility of each dwelling. The results show that river views were available for all dwellings with the simple layout scheme; however, the complex layout scheme was polarized, with 3% of the dwellings having no river views, and a higher number of dwellings with high-quality river-view visibilities. The optimized layout scheme was based on repeated adjustments of the river-view visibility for all dwellings. The viewpoint clouds of the river views on the dwelling exterior walls are described for facade design guidance. The river-view measurement approach can accurately and efficiently measure the river-view visibility of each dwelling in the block, which can be used in optimizing of neighborhood block design.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Urban and Rural Development)
►▼
Show Figures Xijun Hu
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7059; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097059 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
Line-of-sight occlusion in compact cities commonly reduces the river views of riverfront residents. This study developed a new approach to measure the river-view visibilities of individual dwellings in urban riverfront neighborhood blocks. The objective of this study is to achieve a good integration
[...] Read more.
Line-of-sight occlusion in compact cities commonly reduces the river views of riverfront residents. This study developed a new approach to measure the river-view visibilities of individual dwellings in urban riverfront neighborhood blocks. The objective of this study is to achieve a good integration between the morphology of building groups and the ideal river-view visibility of dwellings, and to provide assistance in building and landscape design through the proposed method. First, a design case of an actual riverside neighborhood block with two initial building layout schemes was selected. The complex layout scheme led to a better building-group morphology than the simple layout scheme. Second, 3D models were built using the Rhinoceros and Grasshopper software platforms, and 3D isovists were generated on the hypothetical River Surface Curve (RSC) equipartition points. Finally, the data from the 3D isovists were used to measure the river-view visibility of each dwelling. The results show that river views were available for all dwellings with the simple layout scheme; however, the complex layout scheme was polarized, with 3% of the dwellings having no river views, and a higher number of dwellings with high-quality river-view visibilities. The optimized layout scheme was based on repeated adjustments of the river-view visibility for all dwellings. The viewpoint clouds of the river views on the dwelling exterior walls are described for facade design guidance. The river-view measurement approach can accurately and efficiently measure the river-view visibility of each dwelling in the block, which can be used in optimizing of neighborhood block design.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Urban and Rural Development)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessArticle Twenty Years of Research on Millennials at Work: A Structural Review Using Bibliometric and Content Analysis by Kamal Badar and Kamal Badar and  Karin Lasthuizen
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7058; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097058 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
This study reviews the literature regarding millennials at work over the past 20 years (from 2000 to 2020). Bibliometric methods of citation, co-citation and bibliographic coupling analysis, as well as traditional content analyses, were performed on a sample of 377 articles retrieved from
[...] Read more.
This study reviews the literature regarding millennials at work over the past 20 years (from 2000 to 2020). Bibliometric methods of citation, co-citation and bibliographic coupling analysis, as well as traditional content analyses, were performed on a sample of 377 articles retrieved from ISI Web of Science (WOS). Citation analysis revealed influential articles, authors, journals and countries. Co-citation analysis and bibliographic coupling identified six historic research streams and four current research fronts. The content analysis finally led to the identification of the future research questions. The study explores the body of literature on millennials at work over the last 20 years and offers context and placement in the literature for prior studies by presenting the historical and current state of research. Further, recommended research questions are identified for future research. Finally, we present implications for HRM practice and research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Towards Sustainable HRM: Types, Factors, Drivers and Outcomes)
►▼
Show Figures Karin Lasthuizen
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7058; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097058 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
This study reviews the literature regarding millennials at work over the past 20 years (from 2000 to 2020). Bibliometric methods of citation, co-citation and bibliographic coupling analysis, as well as traditional content analyses, were performed on a sample of 377 articles retrieved from
[...] Read more.
This study reviews the literature regarding millennials at work over the past 20 years (from 2000 to 2020). Bibliometric methods of citation, co-citation and bibliographic coupling analysis, as well as traditional content analyses, were performed on a sample of 377 articles retrieved from ISI Web of Science (WOS). Citation analysis revealed influential articles, authors, journals and countries. Co-citation analysis and bibliographic coupling identified six historic research streams and four current research fronts. The content analysis finally led to the identification of the future research questions. The study explores the body of literature on millennials at work over the last 20 years and offers context and placement in the literature for prior studies by presenting the historical and current state of research. Further, recommended research questions are identified for future research. Finally, we present implications for HRM practice and research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Towards Sustainable HRM: Types, Factors, Drivers and Outcomes)
►▼
Show Figures
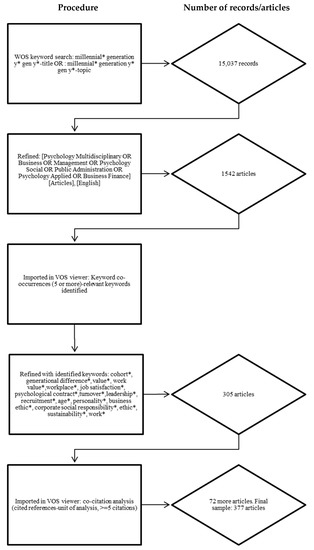 Figure 1 get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessReview Knowledge Mapping of the Rural Teacher Development Policy in China: A Bibliometric Analysis on Web of Science by Jian Li, Jian Li,  Eryong Xue, Eryong Xue,  Jing Cao, Jing Cao,  Yunshu He, Yunshu He,  Yuwei Wu and Yuwei Wu and  Huijie Hou
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7057; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097057 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
The rural teacher development policy plays a key role in cultivating high-quality and sufficient rural teachers in China. This study aims to apply a bibliometric analysis to explore the rural teacher development policy in China’s current education system. The advanced retrieval function of
[...] Read more.
The rural teacher development policy plays a key role in cultivating high-quality and sufficient rural teachers in China. This study aims to apply a bibliometric analysis to explore the rural teacher development policy in China’s current education system. The advanced retrieval function of Web of Science (WoS) is used for the literature data, the core collection of Web of Science is selected for the database, and the time span of literature retrieval is consistent with the selected literature. We apply Citespace to analyze the spatial dimension, research paradigm and research method, research theme, research hotspots and co-occurrence of keywords, the evolution process of research hotspots and content of rural teacher development policy in China. It is found that with the deepening of the reform and development of rural elementary education, scholars not only pay attention to the exploration of the deep mechanism of rural teacher policy, but also to data-oriented diversified empirical research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Education and Approaches)
►▼
Show Figures Huijie Hou
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7057; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097057 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
The rural teacher development policy plays a key role in cultivating high-quality and sufficient rural teachers in China. This study aims to apply a bibliometric analysis to explore the rural teacher development policy in China’s current education system. The advanced retrieval function of
[...] Read more.
The rural teacher development policy plays a key role in cultivating high-quality and sufficient rural teachers in China. This study aims to apply a bibliometric analysis to explore the rural teacher development policy in China’s current education system. The advanced retrieval function of Web of Science (WoS) is used for the literature data, the core collection of Web of Science is selected for the database, and the time span of literature retrieval is consistent with the selected literature. We apply Citespace to analyze the spatial dimension, research paradigm and research method, research theme, research hotspots and co-occurrence of keywords, the evolution process of research hotspots and content of rural teacher development policy in China. It is found that with the deepening of the reform and development of rural elementary education, scholars not only pay attention to the exploration of the deep mechanism of rural teacher policy, but also to data-oriented diversified empirical research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Education and Approaches)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessArticle Beyond Protection: Recognizing Nature’s Rights to Conserve Sharks by Rachel Bustamante
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7056; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097056 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
This paper blends conservation science with legal and policy analysis to assess the primary threats to global shark populations and explores innovative approaches to conservation building upon the philosophy of Earth law, including the Rights of Nature legal framework. Using a case study
[...] Read more.
This paper blends conservation science with legal and policy analysis to assess the primary threats to global shark populations and explores innovative approaches to conservation building upon the philosophy of Earth law, including the Rights of Nature legal framework. Using a case study of Panamá’s national Rights of Nature law, this paper highlights approaches to improve the protection and restoration of shark populations and their habitats. By examining the ecological, social, and economic aspects of conservation holistically, this study offers an interdisciplinary perspective on the urgency for shark protection and presents Rights of Nature as a valuable approach to shark conservation, with potential applications to other species globally.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Shark Conservation: Latest Advances and Prospects)
attachment
Supplementary material:
Supplementary File 1 (ZIP, 561 KiB)
get_app
subject
View online as:
Abstract Page
Full-Text HTML
Open AccessSystematic Review
Progress by Research to Achieve the Sustainable Development Goals in the EU: A Systematic Literature Review
by Rachel Bustamante
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7056; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097056 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
This paper blends conservation science with legal and policy analysis to assess the primary threats to global shark populations and explores innovative approaches to conservation building upon the philosophy of Earth law, including the Rights of Nature legal framework. Using a case study
[...] Read more.
This paper blends conservation science with legal and policy analysis to assess the primary threats to global shark populations and explores innovative approaches to conservation building upon the philosophy of Earth law, including the Rights of Nature legal framework. Using a case study of Panamá’s national Rights of Nature law, this paper highlights approaches to improve the protection and restoration of shark populations and their habitats. By examining the ecological, social, and economic aspects of conservation holistically, this study offers an interdisciplinary perspective on the urgency for shark protection and presents Rights of Nature as a valuable approach to shark conservation, with potential applications to other species globally.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Shark Conservation: Latest Advances and Prospects)
attachment
Supplementary material:
Supplementary File 1 (ZIP, 561 KiB)
get_app
subject
View online as:
Abstract Page
Full-Text HTML
Open AccessSystematic Review
Progress by Research to Achieve the Sustainable Development Goals in the EU: A Systematic Literature Review
by
 Matteo Trane, Matteo Trane,  Luisa Marelli, Luisa Marelli,  Alice Siragusa, Alice Siragusa,  Riccardo Pollo and Riccardo Pollo and  Patrizia Lombardi
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7055; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097055 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
Scientific research has been acknowledged to play a pivotal role in achieving the United Nations’ 2030 Agenda. Vice-versa, since its adoption, the 2030 Agenda has been reinvigorating the academic production on sustainable development. This study provides a systematic literature review of the most
[...] Read more.
Scientific research has been acknowledged to play a pivotal role in achieving the United Nations’ 2030 Agenda. Vice-versa, since its adoption, the 2030 Agenda has been reinvigorating the academic production on sustainable development. This study provides a systematic literature review of the most used and newly developed approaches by academic research to support the achievement of the SDGs in the EU. The results are presented by descriptive, bibliometric, and content analysis. The descriptive analysis highlights a rising interest of scholars in operationalizing the 2030 Agenda, with a growing interest at the urban level. A text-mining tool was employed to scan the most investigated SDGs in the selected papers. Major interest by scholars is devoted to environmental concerns (especially linked to SDG 13, 7, 6, 12, and 15), while social issues (e.g., SDG 4, 5, and 10) still deserve more research. The bibliometric analysis unveiled poor intra-cluster connections, highlighting the need for more transdisciplinary research. The most recurrent research fields on the SDGs in the EU are governance, circular economy, ecosystem services, urban localization, and decision making. We advise future studies to focus on gaps highlighted and adopt a system perspective, boosting Policy Coherence across governance levels and scales of implementation by looking at trade-offs and assessing context-specific priorities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Environmental Governance for Sustainable Development)
►▼
Show Figures Patrizia Lombardi
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7055; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097055 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
Scientific research has been acknowledged to play a pivotal role in achieving the United Nations’ 2030 Agenda. Vice-versa, since its adoption, the 2030 Agenda has been reinvigorating the academic production on sustainable development. This study provides a systematic literature review of the most
[...] Read more.
Scientific research has been acknowledged to play a pivotal role in achieving the United Nations’ 2030 Agenda. Vice-versa, since its adoption, the 2030 Agenda has been reinvigorating the academic production on sustainable development. This study provides a systematic literature review of the most used and newly developed approaches by academic research to support the achievement of the SDGs in the EU. The results are presented by descriptive, bibliometric, and content analysis. The descriptive analysis highlights a rising interest of scholars in operationalizing the 2030 Agenda, with a growing interest at the urban level. A text-mining tool was employed to scan the most investigated SDGs in the selected papers. Major interest by scholars is devoted to environmental concerns (especially linked to SDG 13, 7, 6, 12, and 15), while social issues (e.g., SDG 4, 5, and 10) still deserve more research. The bibliometric analysis unveiled poor intra-cluster connections, highlighting the need for more transdisciplinary research. The most recurrent research fields on the SDGs in the EU are governance, circular economy, ecosystem services, urban localization, and decision making. We advise future studies to focus on gaps highlighted and adopt a system perspective, boosting Policy Coherence across governance levels and scales of implementation by looking at trade-offs and assessing context-specific priorities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Environmental Governance for Sustainable Development)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessPerspective Learning from the Future of Kuwait: Scenarios as a Learning Tool to Build Consensus for Actions Needed to Realize Vision 2035 by Andri Ottesen, Andri Ottesen,  Dieter Thom, Dieter Thom,  Rupali Bhagat and Rupali Bhagat and  Rola Mourdaa
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7054; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097054 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
This perspective is a qualitative meta-analysis study using a critical interpretive synthesis that narrates three future and equally plausible scenarios of social and economic development in the State of Kuwait over the next 15 years. The first scenario follows what we call the
[...] Read more.
This perspective is a qualitative meta-analysis study using a critical interpretive synthesis that narrates three future and equally plausible scenarios of social and economic development in the State of Kuwait over the next 15 years. The first scenario follows what we call the ‘Sustainable Growth’ model as defined by the United Nations Development Goals and the Kuwait Vision 2035 presented by the Amir Sheikh Sabah Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah. As a polar opposite, the next scenario is what we call the ‘Mismanaged Resourced-Based Autocracy’ model, a negative reflection of the worst-case scenario. The third scenario is in between these two, and we call it the ‘Equality of Outcome Between Societal Groups’ model. So as not to lay blame for past actions or point fingers, which could prove counterproductive to a consensus-building process for needed actions, we chose to use the pasts of other countries for future projections for the State of Kuwait. Our search through recent socio-economic pasts revealed that Singapore was the best fit for the first scenario, Venezuela for the second, and Lebanon for the third. All these countries became fully independent at approximately the same time as the State of Kuwait and share many other similarities. The three future projections were used as input variables to the outcome, which was a bottom-up and top-down consensus-making process regarding utilitarian action for Kuwait to be used by Non-Government Organizations (NGOs), Think-Tanks, Development Agencies, the government and the parliament.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Economic and Business Aspects of Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures Rola Mourdaa
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7054; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097054 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
This perspective is a qualitative meta-analysis study using a critical interpretive synthesis that narrates three future and equally plausible scenarios of social and economic development in the State of Kuwait over the next 15 years. The first scenario follows what we call the
[...] Read more.
This perspective is a qualitative meta-analysis study using a critical interpretive synthesis that narrates three future and equally plausible scenarios of social and economic development in the State of Kuwait over the next 15 years. The first scenario follows what we call the ‘Sustainable Growth’ model as defined by the United Nations Development Goals and the Kuwait Vision 2035 presented by the Amir Sheikh Sabah Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah. As a polar opposite, the next scenario is what we call the ‘Mismanaged Resourced-Based Autocracy’ model, a negative reflection of the worst-case scenario. The third scenario is in between these two, and we call it the ‘Equality of Outcome Between Societal Groups’ model. So as not to lay blame for past actions or point fingers, which could prove counterproductive to a consensus-building process for needed actions, we chose to use the pasts of other countries for future projections for the State of Kuwait. Our search through recent socio-economic pasts revealed that Singapore was the best fit for the first scenario, Venezuela for the second, and Lebanon for the third. All these countries became fully independent at approximately the same time as the State of Kuwait and share many other similarities. The three future projections were used as input variables to the outcome, which was a bottom-up and top-down consensus-making process regarding utilitarian action for Kuwait to be used by Non-Government Organizations (NGOs), Think-Tanks, Development Agencies, the government and the parliament.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Economic and Business Aspects of Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 attachment Supplementary material: Supplementary File 1 (ZIP, 30 KiB) get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessArticle Methane Anaerobic Oxidation Potential and Microbial Community Response to Sulfate Input in Coastal Wetlands of the Yellow River Delta by Jun Li, Jun Li,  Qingfeng Chen, Qingfeng Chen,  Xinghua Wang, Xinghua Wang,  Yu Tan, Yu Tan,  Luzhen Li, Luzhen Li,  Bowei Zhang, Bowei Zhang,  Beibei Guo and Beibei Guo and  Changsheng Zhao
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7053; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097053 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
In the context of global warming and carbon neutrality, reducing greenhouse gas emissions is fundamental to achieving sustainable development. As an important greenhouse gas, methane has a much stronger warming effect than CO2, and studies have demonstrated that anaerobic oxidation of
[...] Read more.
In the context of global warming and carbon neutrality, reducing greenhouse gas emissions is fundamental to achieving sustainable development. As an important greenhouse gas, methane has a much stronger warming effect than CO2, and studies have demonstrated that anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM) is important for global methane emissions. This paper systematically investigated the AOM potential and microbial community response to the input of SO42− in the three typical salt marsh soils of the Yellow River Delta: Reed, Suaeda salsa, and Tamarisk, using SO42− as the electron acceptor and a combination of indoor anaerobic culture and high-throughput sequencing. The results showed that after adding an appropriate concentration of SO42−, the AOM potential was significantly promoted in Tamarix soil (p < 0.05) and significantly inhibited in Reed and Suaeda salsa soil (p < 0.05); soil AOM potential and SO42− input concentration and background values were correlated. At the microbial level, SO42− input affected the abundance of some microorganisms. At the phylum level, the relative abundance of Proteobacteria was increased in Suaeda salsa soil, decreased in Tamarisk soil, and did not change significantly in Reed soil; that of Crenarchaeota and Desulfobacterota was significantly increased in Tamarisk soil. At the genus level, Methylophaga, Methylotenera, and Methylomonaceae became the dominant populations, and it can be inferred that these bacteria are involved in the anaerobic oxidation of methane after the input of SO42−. This study will be of great significance to the mechanistic study of AOM and the conservation of microbial diversity in the Yellow River Delta Coastal Wetland, as well as provide a scientific basis for CH4 reduction in coastal wetlands.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Soil Carbon Sequestration and Greenhouse Gas Emission)
►▼
Show Figures Changsheng Zhao
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7053; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097053 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
In the context of global warming and carbon neutrality, reducing greenhouse gas emissions is fundamental to achieving sustainable development. As an important greenhouse gas, methane has a much stronger warming effect than CO2, and studies have demonstrated that anaerobic oxidation of
[...] Read more.
In the context of global warming and carbon neutrality, reducing greenhouse gas emissions is fundamental to achieving sustainable development. As an important greenhouse gas, methane has a much stronger warming effect than CO2, and studies have demonstrated that anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM) is important for global methane emissions. This paper systematically investigated the AOM potential and microbial community response to the input of SO42− in the three typical salt marsh soils of the Yellow River Delta: Reed, Suaeda salsa, and Tamarisk, using SO42− as the electron acceptor and a combination of indoor anaerobic culture and high-throughput sequencing. The results showed that after adding an appropriate concentration of SO42−, the AOM potential was significantly promoted in Tamarix soil (p < 0.05) and significantly inhibited in Reed and Suaeda salsa soil (p < 0.05); soil AOM potential and SO42− input concentration and background values were correlated. At the microbial level, SO42− input affected the abundance of some microorganisms. At the phylum level, the relative abundance of Proteobacteria was increased in Suaeda salsa soil, decreased in Tamarisk soil, and did not change significantly in Reed soil; that of Crenarchaeota and Desulfobacterota was significantly increased in Tamarisk soil. At the genus level, Methylophaga, Methylotenera, and Methylomonaceae became the dominant populations, and it can be inferred that these bacteria are involved in the anaerobic oxidation of methane after the input of SO42−. This study will be of great significance to the mechanistic study of AOM and the conservation of microbial diversity in the Yellow River Delta Coastal Wetland, as well as provide a scientific basis for CH4 reduction in coastal wetlands.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Soil Carbon Sequestration and Greenhouse Gas Emission)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessArticle The Moderating Role of Digital Environmental Management Accounting in the Relationship between Eco-Efficiency and Corporate Sustainability by Abeer M. Abdelhalim, Abeer M. Abdelhalim,  Nahla Ibrahim and Nahla Ibrahim and  Mohammed Alomair
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7052; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097052 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
In response to concerns about environmental issues and the role of manufacturing corporations in maintaining eco-efficiency, this study aimed to investigate the moderating role of digitally supported environmental management accounting (EMA) in the relationship between eco-efficiency and corporate sustainability performance. A quantitative approach
[...] Read more.
In response to concerns about environmental issues and the role of manufacturing corporations in maintaining eco-efficiency, this study aimed to investigate the moderating role of digitally supported environmental management accounting (EMA) in the relationship between eco-efficiency and corporate sustainability performance. A quantitative approach was applied by using a survey distributed to a sample consisting of 77 individuals from senior and executive financial and operational positions in large Saudi manufacturing corporations. The findings of the linear regression analysis revealed that there is an insignificant direct relationship between eco-efficiency and corporate sustainability performance, while there is a significant moderating impact of EMA on the linkage between eco-efficiency and corporate environmental sustainability, and this significant moderating impact also applied to the linkage between digital applications and corporate environmental sustainability. This study provides good insights into the domain of environmental sustainability performance on the business scale in the Saudi context as an emerging economy, as it could be considered an innovative contribution to theoretical and practical aspects in the recent green issue adoption context; theoretically, it provides additional evidence of the role of digital EMA in improving environmental sustainability performance, and practically, the study findings can be beneficial for strategy and policymakers in corporations and regulators of environmental sustainability performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Accounting, Corporate Policies and Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures Mohammed Alomair
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7052; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097052 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
In response to concerns about environmental issues and the role of manufacturing corporations in maintaining eco-efficiency, this study aimed to investigate the moderating role of digitally supported environmental management accounting (EMA) in the relationship between eco-efficiency and corporate sustainability performance. A quantitative approach
[...] Read more.
In response to concerns about environmental issues and the role of manufacturing corporations in maintaining eco-efficiency, this study aimed to investigate the moderating role of digitally supported environmental management accounting (EMA) in the relationship between eco-efficiency and corporate sustainability performance. A quantitative approach was applied by using a survey distributed to a sample consisting of 77 individuals from senior and executive financial and operational positions in large Saudi manufacturing corporations. The findings of the linear regression analysis revealed that there is an insignificant direct relationship between eco-efficiency and corporate sustainability performance, while there is a significant moderating impact of EMA on the linkage between eco-efficiency and corporate environmental sustainability, and this significant moderating impact also applied to the linkage between digital applications and corporate environmental sustainability. This study provides good insights into the domain of environmental sustainability performance on the business scale in the Saudi context as an emerging economy, as it could be considered an innovative contribution to theoretical and practical aspects in the recent green issue adoption context; theoretically, it provides additional evidence of the role of digital EMA in improving environmental sustainability performance, and practically, the study findings can be beneficial for strategy and policymakers in corporations and regulators of environmental sustainability performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Accounting, Corporate Policies and Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app subject View online as: Abstract Page Full-Text HTML Open AccessArticle Productive Service Agglomeration, Human Capital Level, and Urban Economic Performance by Du Peng, Du Peng,  Ehsan Elahi and Ehsan Elahi and  Zainab Khalid
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7051; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097051 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
This study aims to investigate the impact of productive service industry agglomeration on the economic performance of Chinese cities. The study analyzes data from 285 prefecture-level cities over a 16-year period (2003–2019) and develops a comprehensive urban economic index evaluation system based on
[...] Read more.
This study aims to investigate the impact of productive service industry agglomeration on the economic performance of Chinese cities. The study analyzes data from 285 prefecture-level cities over a 16-year period (2003–2019) and develops a comprehensive urban economic index evaluation system based on three dimensions: social, economic, and resource and environmental benefits. The empirical analysis reveals that high-end productive service industry agglomeration has a significant positive relationship with urban economic performance (effect size of 0.012), whereas low-end productive service industry agglomeration does not. The study also finds that the impact of productive service industry agglomeration on economic performance varies across different regions and cities. Specifically, productive service industry agglomeration has a significant positive impact on the economic performance of cities in the eastern, central, northeastern, and western regions, with the impact being twice as much in the western region compared to the eastern region. Moreover, the effect of productive service industry agglomeration on the economic performance of non-resource-based cities is almost one-third more than that of resource-based cities. The study further reveals that human capital plays a mediating role in the relationship between productive service industry agglomeration and urban economic performance. Based on these findings, the study suggests that Chinese cities, particularly non-resource-based cities and those in the central and western regions, should focus on supporting high-end productive service industry agglomeration, improve the quality of productive service industry agglomeration, strengthen the matching between the accumulation of human capital and the development of productive service industry agglomeration, and tailor their strategies to promote the development of productive service industry agglomeration effectively to improve their economic performance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures Zainab Khalid
Sustainability 2023, 15(9), 7051; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097051 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2023
Abstract
This study aims to investigate the impact of productive service industry agglomeration on the economic performance of Chinese cities. The study analyzes data from 285 prefecture-level cities over a 16-year period (2003–2019) and develops a comprehensive urban economic index evaluation system based on
[...] Read more.
This study aims to investigate the impact of productive service industry agglomeration on the economic performance of Chinese cities. The study analyzes data from 285 prefecture-level cities over a 16-year period (2003–2019) and develops a comprehensive urban economic index evaluation system based on three dimensions: social, economic, and resource and environmental benefits. The empirical analysis reveals that high-end productive service industry agglomeration has a significant positive relationship with urban economic performance (effect size of 0.012), whereas low-end productive service industry agglomeration does not. The study also finds that the impact of productive service industry agglomeration on economic performance varies across different regions and cities. Specifically, productive service industry agglomeration has a significant positive impact on the economic performance of cities in the eastern, central, northeastern, and western regions, with the impact being twice as much in the western region compared to the eastern region. Moreover, the effect of productive service industry agglomeration on the economic performance of non-resource-based cities is almost one-third more than that of resource-based cities. The study further reveals that human capital plays a mediating role in the relationship between productive service industry agglomeration and urban economic performance. Based on these findings, the study suggests that Chinese cities, particularly non-resource-based cities and those in the central and western regions, should focus on supporting high-end productive service industry agglomeration, improve the quality of productive service industry agglomeration, strengthen the matching between the accumulation of human capital and the development of productive service industry agglomeration, and tailor their strategies to promote the development of productive service industry agglomeration effectively to improve their economic performance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 More Articles... Submit to Sustainability
Review for Sustainability
Share
Journal Menu
►
▼
Journal Menu
Sustainability Home
Aims & Scope
Editorial Board
Reviewer Board
Topical Advisory Panel
Instructions for Authors
Special Issues
Topics
Sections & Collections
Article Processing Charge
Indexing & Archiving
Editor's Choice Articles
Most Cited & Viewed
Journal Statistics
Journal History
Journal Awards
Society Collaborations
Conferences
Editorial Office
Journal Browser
►
▼
Journal Browser
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios
Current issue
Vol. 15 (2023)
Vol. 14 (2022)
Vol. 13 (2021)
Vol. 12 (2020)
Vol. 11 (2019)
Vol. 10 (2018)
Vol. 9 (2017)
Vol. 8 (2016)
Vol. 7 (2015)
Vol. 6 (2014)
Vol. 5 (2013)
Vol. 4 (2012)
Vol. 3 (2011)
Vol. 2 (2010)
Vol. 1 (2009)
Highly Accessed Articles
View More...
Latest Books
More Open Access Books...
E-Mail Alert
News
11 April 2023
Meet Us at the 2023 Science and Technology Annual Meeting of Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences, 22–23 April 2023, Nanchang, China
Submit to Sustainability
Review for Sustainability
Share
Journal Menu
►
▼
Journal Menu
Sustainability Home
Aims & Scope
Editorial Board
Reviewer Board
Topical Advisory Panel
Instructions for Authors
Special Issues
Topics
Sections & Collections
Article Processing Charge
Indexing & Archiving
Editor's Choice Articles
Most Cited & Viewed
Journal Statistics
Journal History
Journal Awards
Society Collaborations
Conferences
Editorial Office
Journal Browser
►
▼
Journal Browser
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios
Current issue
Vol. 15 (2023)
Vol. 14 (2022)
Vol. 13 (2021)
Vol. 12 (2020)
Vol. 11 (2019)
Vol. 10 (2018)
Vol. 9 (2017)
Vol. 8 (2016)
Vol. 7 (2015)
Vol. 6 (2014)
Vol. 5 (2013)
Vol. 4 (2012)
Vol. 3 (2011)
Vol. 2 (2010)
Vol. 1 (2009)
Highly Accessed Articles
View More...
Latest Books
More Open Access Books...
E-Mail Alert
News
11 April 2023
Meet Us at the 2023 Science and Technology Annual Meeting of Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences, 22–23 April 2023, Nanchang, China
 29 March 2023
Meet Us at the 6th International Conference on Natural Fibers, 19–21 June 2023, Funchal, Portugal
29 March 2023
Meet Us at the 6th International Conference on Natural Fibers, 19–21 June 2023, Funchal, Portugal
 17 March 2023
Meet Us at the Joint Conference on Environmental Chemicals Japan 2023, 30 May–2 June 2023, Tokushima, Japan
17 March 2023
Meet Us at the Joint Conference on Environmental Chemicals Japan 2023, 30 May–2 June 2023, Tokushima, Japan
 More News & Announcements...
Topics
Edit a Topic
Topic in
Sustainability, Buildings, Energies, Urban Science, Environments
Sustainable Built Environment
Topic Editors: Siu-Kit Lau, Vesna Kosorić, Abel Tablada, Zdravko Trivic, Miljana Horvat, Milena Vukmirović, Silvia Domingo-Irigoyen, Marija Todorović, Jérôme H. Kaempf, Kosa Golić, Ana PericDeadline: 30 April 2023
Topic in
Acoustics, Buildings, CivilEng, Climate, Energies, Environments, IJERPH, Sustainability
Built Environment and Human Comfort
Topic Editors: Wei Liu, Manuel Carlos Gameiro da Silva, Dayi LaiDeadline: 20 May 2023
Topic in
Geosciences, Hydrology, Remote Sensing, Sustainability, Water
Hydrological Modeling and Engineering: Managing Risk and Uncertainties
Topic Editors: Md Jahangir Alam, Monzur Imteaz, Abdallah ShanblehDeadline: 31 May 2023
Topic in
Current Oncology, Genealogy, Healthcare, Pharmacy, Safety, Sustainability, TropicalMed
Cultural Safety – towards a Global Research Agenda
Topic Editors: Mark Lock, Teresa Brockie, Vicki KerriganDeadline: 15 June 2023
More Topics
More News & Announcements...
Topics
Edit a Topic
Topic in
Sustainability, Buildings, Energies, Urban Science, Environments
Sustainable Built Environment
Topic Editors: Siu-Kit Lau, Vesna Kosorić, Abel Tablada, Zdravko Trivic, Miljana Horvat, Milena Vukmirović, Silvia Domingo-Irigoyen, Marija Todorović, Jérôme H. Kaempf, Kosa Golić, Ana PericDeadline: 30 April 2023
Topic in
Acoustics, Buildings, CivilEng, Climate, Energies, Environments, IJERPH, Sustainability
Built Environment and Human Comfort
Topic Editors: Wei Liu, Manuel Carlos Gameiro da Silva, Dayi LaiDeadline: 20 May 2023
Topic in
Geosciences, Hydrology, Remote Sensing, Sustainability, Water
Hydrological Modeling and Engineering: Managing Risk and Uncertainties
Topic Editors: Md Jahangir Alam, Monzur Imteaz, Abdallah ShanblehDeadline: 31 May 2023
Topic in
Current Oncology, Genealogy, Healthcare, Pharmacy, Safety, Sustainability, TropicalMed
Cultural Safety – towards a Global Research Agenda
Topic Editors: Mark Lock, Teresa Brockie, Vicki KerriganDeadline: 15 June 2023
More Topics
 Conferences
Announce Your Conference
14 September 2023
The 10th World Sustainability Forum
Conferences
Announce Your Conference
14 September 2023
The 10th World Sustainability Forum 4 May 2023
2nd International Conference on Technology, Innovation, and Sustainability in Business Management (ICTIS 2023)
4 May 2023
2nd International Conference on Technology, Innovation, and Sustainability in Business Management (ICTIS 2023) 11–12 May 2023
Adaptation Strategies To Reduce Societal Impact Of Climate Change And Coastal Hazards In The UK
11–12 May 2023
Adaptation Strategies To Reduce Societal Impact Of Climate Change And Coastal Hazards In The UK More Conferences...
Special Issues
Edit a Special Issue
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Inventory Management for Sustainable Industrial Operations
Guest Editors: Riccardo Patriarca, Giulio Di Gravio, Francesco CostantinoDeadline: 30 April 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Renewable Energy and Utility System Optimization for Sustainable Industries
Guest Editors: Cristina Rodriguez, Li SunDeadline: 15 May 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Trends in Emerging Markets, Globalization, Economic Development, Entrepreneurship and Management Strategies as a Result of Cross-Border Cooperation
Guest Editors: Rui Alexandre Castanho, Daniel Francois MeyerDeadline: 31 May 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Modern Water/Air Quality Monitoring and Mapping for Sustainable Management
Guest Editor: Hone-Jay ChuDeadline: 15 June 2023
More Special Issues
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Mobile Technology, Gamification and Artificial Intelligence to Improve Sustainability in Education
Collection Editors: Eloy López Meneses, Esteban Vázquez-Cano, María Elena Parra-González
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Sustainable Soil Management in a Changing Climate
Collection Editors: Georgios Koubouris, José Alfonso Gómez, Luuk Fleskens, Giuseppe Montanaro
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Towards More Walkable and Liveable Cities: Perceptions, Attitudes, Methods, Technologies and Policies
Collection Editors: Fernando Fonseca, Paulo Ribeiro, Elisa Conticelli, George N. Papageorgiou
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Supply Chain Innovability: Combining Innovation and Sustainability for the Future of Supply Chains
Collection Editors: Antonella Moretto, Antonio Messeni Petruzzelli, Federico Frattini
More Topical Collections
Sustainability,
EISSN 2071-1050,
Published by MDPI
RSS
Content Alert
Further Information
Article Processing Charges
Pay an Invoice
Open Access Policy
Contact MDPI
Jobs at MDPI
Guidelines
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
MDPI Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
Follow MDPI
LinkedIn
Facebook
Twitter
More Conferences...
Special Issues
Edit a Special Issue
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Inventory Management for Sustainable Industrial Operations
Guest Editors: Riccardo Patriarca, Giulio Di Gravio, Francesco CostantinoDeadline: 30 April 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Renewable Energy and Utility System Optimization for Sustainable Industries
Guest Editors: Cristina Rodriguez, Li SunDeadline: 15 May 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Trends in Emerging Markets, Globalization, Economic Development, Entrepreneurship and Management Strategies as a Result of Cross-Border Cooperation
Guest Editors: Rui Alexandre Castanho, Daniel Francois MeyerDeadline: 31 May 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Modern Water/Air Quality Monitoring and Mapping for Sustainable Management
Guest Editor: Hone-Jay ChuDeadline: 15 June 2023
More Special Issues
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Mobile Technology, Gamification and Artificial Intelligence to Improve Sustainability in Education
Collection Editors: Eloy López Meneses, Esteban Vázquez-Cano, María Elena Parra-González
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Sustainable Soil Management in a Changing Climate
Collection Editors: Georgios Koubouris, José Alfonso Gómez, Luuk Fleskens, Giuseppe Montanaro
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Towards More Walkable and Liveable Cities: Perceptions, Attitudes, Methods, Technologies and Policies
Collection Editors: Fernando Fonseca, Paulo Ribeiro, Elisa Conticelli, George N. Papageorgiou
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Supply Chain Innovability: Combining Innovation and Sustainability for the Future of Supply Chains
Collection Editors: Antonella Moretto, Antonio Messeni Petruzzelli, Federico Frattini
More Topical Collections
Sustainability,
EISSN 2071-1050,
Published by MDPI
RSS
Content Alert
Further Information
Article Processing Charges
Pay an Invoice
Open Access Policy
Contact MDPI
Jobs at MDPI
Guidelines
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
MDPI Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
Follow MDPI
LinkedIn
Facebook
Twitter
 © 1996-2023 MDPI (Basel, Switzerland) unless otherwise stated
Disclaimer
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely
those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or
the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas,
methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
Terms and Conditions
Privacy Policy
We use cookies on our website to ensure you get the best experience.
Read more about our cookies here.
Accept
We have just recently launched a new version of our website.
Help us to further improve by taking part in this short 5 minute survey
here.
here.
Never show this again
Share Link
Copy
clear
Share
https://www.mdpi.com/journal/sustainability
clear
Back to TopTop
© 1996-2023 MDPI (Basel, Switzerland) unless otherwise stated
Disclaimer
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely
those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or
the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas,
methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
Terms and Conditions
Privacy Policy
We use cookies on our website to ensure you get the best experience.
Read more about our cookies here.
Accept
We have just recently launched a new version of our website.
Help us to further improve by taking part in this short 5 minute survey
here.
here.
Never show this again
Share Link
Copy
clear
Share
https://www.mdpi.com/journal/sustainability
clear
Back to TopTop
|
【本文地址】